Unit Name: Phonemic Awareness - Transportation
Vision for the Unit:
The learning should be fun and interactive for the young learners
- At the end of the unit, students are expected to master the basic letter-sound association and learn new vocabulary on transportation
- Students know about letters, words, and sounds. They apply this knowledge to read simple sentences
Summative Assessment:
Standard to be met:
READING: Word Recognition, Fluency, and
Vocabulary Development
Teaching
strategy: ‘Whole Group’ strategy:
1. Group 1 – Small Group and Individual Independent
Work
Group 1 remains on the carpet to work together as a small group sorting out modes of transportation (on land, water and air). Then, they can work with a shaving cream writing activity and/or iPads applications independently (on Phonemes, Sounds and Alphabet formation). They can also listen to some digital nursery rhymes, songs and stories on transportation independently.
Group 2 moves onto Table 1 to work with Teacher 1 using the ‘No-opt-out’ strategy for reinforcement of the taught lesson using picture word flash cards (on print). After that, they can use the iPad vocabulary apps and sort out modes of transportation with a partner. A sand table writing activity is provided for alphabet formation practice.
3. Group 3 – Teacher-assisted Individual and Small Group work
Group 3 moves onto Table 2 to work with Teacher 2 using the ‘No-opt-out’ strategy for reinforcement of the taught lesson. Reinforcement will be conducted mainly through the ‘One-on-One’ strategy. For these students with limited knowledge and short attention span, the iPads will be used to attract their attention and keep them focused, as much as possible. They will start by looking at digital picture word flash cards. They will listen to the vocabulary and repeat after the teacher / iPad app. They will play ‘sorting vehicles inside the circle’ game as a small group, with the teacher.
1. After the differentiated activities, have the
students to come back to the carpet and do ‘show and tell’ with the first
letter of a vehicle they have picked. For example, ‘This is a tractor. Tractor
begins with T - t,t,t, tractor.’
2. To end the lesson, students will watch and sing along to some online phonics and transportation songs, integrating TPR and Counting skills:
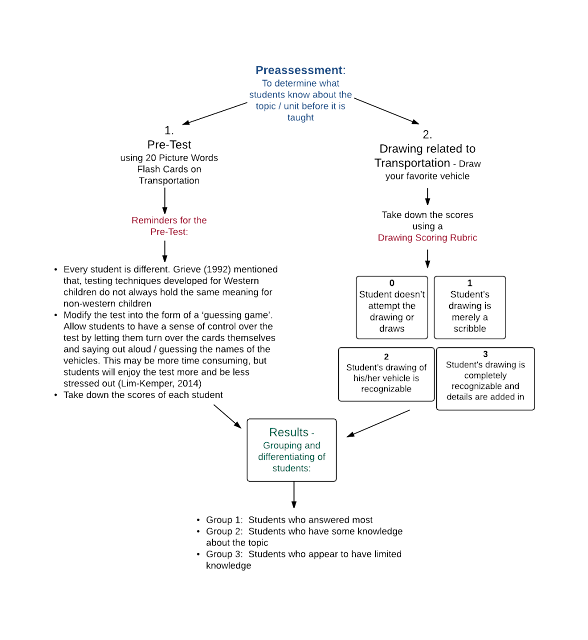
Why is Preassessment important?
Pre-assessment allows the teacher and student to discover what is
already known in a specific topic or subject. It is critical to recognize prior
knowledge so students can engage in questioning, formulating, thinking and
theorizing in order to construct new knowledge appropriate to their level.
Ongoing assessment throughout the learning process is also critical as it
directs the teacher and student as to where to go next. Two assessment
techniques are described in my Flowchart.
Teaching
strategy: ‘Whole Group’ strategy:
- Start the lesson on the carpet by introducing the unit on Transportation
- Ask students about their favorite mode of transportation
- For the high-flyers, extend the discussion with the ‘Stretch it’ strategy
- Use picture word flash cards to learn new sounds and vocabulary
- Use the ‘I Do, We Do, You Do’ strategy for the whole class
- For students who are not following, repeat with the ‘No-opt-out’ strategy
- Do air-writing altogether for correct formation of alphabets
- Break into small groups
Innovative and differentiated Teaching Strategies and Activities for the three groups of students:
Group 1 remains on the carpet to work together as a small group sorting out modes of transportation (on land, water and air). Then, they can work with a shaving cream writing activity and/or iPads applications independently (on Phonemes, Sounds and Alphabet formation). They can also listen to some digital nursery rhymes, songs and stories on transportation independently.
2. Group 2 – Teacher-assisted Partner and Individual
Work
Group 2 moves onto Table 1 to work with Teacher 1 using the ‘No-opt-out’ strategy for reinforcement of the taught lesson using picture word flash cards (on print). After that, they can use the iPad vocabulary apps and sort out modes of transportation with a partner. A sand table writing activity is provided for alphabet formation practice.
3. Group 3 – Teacher-assisted Individual and Small Group work
Group 3 moves onto Table 2 to work with Teacher 2 using the ‘No-opt-out’ strategy for reinforcement of the taught lesson. Reinforcement will be conducted mainly through the ‘One-on-One’ strategy. For these students with limited knowledge and short attention span, the iPads will be used to attract their attention and keep them focused, as much as possible. They will start by looking at digital picture word flash cards. They will listen to the vocabulary and repeat after the teacher / iPad app. They will play ‘sorting vehicles inside the circle’ game as a small group, with the teacher.
Wrapping up the lesson with the ‘Whole Group’ strategy:
2. To end the lesson, students will watch and sing along to some online phonics and transportation songs, integrating TPR and Counting skills:
Tracking and improving students’ learning through Strategies used:
- All activities conducted in the lesson(s) use the ‘I Do, We Do, You Do’ strategy, as a lot of modeling is involved in teaching very young learners
- Every lesson will begin with a whole class activity, to provide every student the opportunity to experience the ‘whole class instruction’ using the ‘I Do, We Do, You Do’ strategy
- The ‘whole class instruction’ allows every student to learn and experience working as a group. Students develop their ability to listen and pay attention to what someone else is saying, get along with, be patient and cooperate with other students and also follow simple rules
- The ‘whole class instruction’ also allow the weaker students to learn by ‘copying’ what the stronger one is doing
- This student-centered approach helps students to develop a ‘can-do’ attitude
(Accessed on 29 June 2015)
- http://www.wku.edu/rtwsc/documents/exemplars/ex-9.pdf
- https://kendrik2.wordpress.com/2007/09/27/pre-assessment-strategies/
- Grieve, K.W. (1992). Play based assessment of the cognitive abilities of young children. Pp. 5.6-5.21. Unpublished doctoral thesis, Unisa, Pretoria
- Lim-Kemper, D. (2014) Can songs increase the English vocabulary learning of a group of mixed first language children attending an international school in Germany? MA in Education Research Project, Birmingham City University. Available at: https://www.academia.edu/9435217/Can_songs_increase_the_English_vocabulary_learning_of_a_group_of_mixed_first_language_children_attending_an_international_school_in_Germany